The capacity to download a HD feature film in three seconds, mobile data streaming speeds that surpass home internet speeds, and a farewell to data limits on cell phone plans.
If you’re like me then you’ve read a lot about 5G technology and the promise for consumers seems clear, but how will 5G technology impact the world of IoT, and should IoT vendors make the switch?
What is 5G?
 The first generation of wireless connectivity carried voice across analog radio signals. Second and third generation wireless networks digitized those communications and added the capacity to transmit mobile data, if at relatively low speeds. As Wired explains, 3G wireless ushered in the era of the smartphone and a first generation of IoT devices. With an upgrade to fourth generation, or 4G, technology, network speed and data transfer capacity jumped significantly, from 42 Mbps to 150 Mbps.
The first generation of wireless connectivity carried voice across analog radio signals. Second and third generation wireless networks digitized those communications and added the capacity to transmit mobile data, if at relatively low speeds. As Wired explains, 3G wireless ushered in the era of the smartphone and a first generation of IoT devices. With an upgrade to fourth generation, or 4G, technology, network speed and data transfer capacity jumped significantly, from 42 Mbps to 150 Mbps.
The arrival of 5G wireless networks, though, make even that capacity look pedestrian.
5G networks are expected to be “600 times faster than the typical 4G speeds on today’s mobile phones, and 10 times faster than Google Fiber’s standard home broadband service”.
The 5G roll-out is already underway in North America, Europe, and Asia, and its launch proper in 2020 and 2021 will offer significant opportunities for IoT vendors to expand the scope, reach, and utility of their offer.
Reaping the benefits of 5G

While autonomous vehicles have been a goal of auto manufacturers globally, 5G is expected to expand the efficiency of the vehicles and improve traffic flows, too. 5G wireless connectivity between vehicles will allow for cars, trucks, and buses to form aerodynamically efficient ‘schools’ that move fluidly along roadways with mere meters between each car. Relying on a wider traffic network of IoT sensors and monitoring devices, 5G connected autonomous vehicles will offer a break from driving and the potential for both lower fuel bills and the end of traffic jams.
 The industrial IoT (IIoT) sector is also expected to benefit from 5G technology. KPMG, for example, speaks of a “hyper-connected enterprise” where workers equipped with augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR) headsets will be free to move about the factory floor, connected at all times to the 5G network. These workers will interact with IoT devices and data and simulate every process in three dimensions. As KPMG notes, since even the smallest mistake in design or layout can be expensive, AR/VR’s ability to spot potential errors through simulations is a valuable attribute of this new 5G-enabled system.
The industrial IoT (IIoT) sector is also expected to benefit from 5G technology. KPMG, for example, speaks of a “hyper-connected enterprise” where workers equipped with augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR) headsets will be free to move about the factory floor, connected at all times to the 5G network. These workers will interact with IoT devices and data and simulate every process in three dimensions. As KPMG notes, since even the smallest mistake in design or layout can be expensive, AR/VR’s ability to spot potential errors through simulations is a valuable attribute of this new 5G-enabled system.
…But Drawbacks Remain
Yet for all the promise of 5G, I think that there are some drawbacks to consider, too.
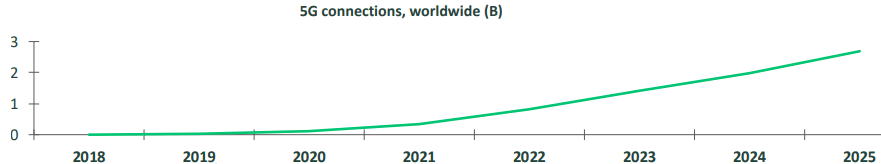
For one, the roll-out of 5G remains slow. While there have been tests worldwide and much hype about 5G-enabled technologies, there isn’t much in the way of a true, large-scale 5G network. While there are expected to be 340 million 5G connections in 2021, this pales in comparison to the 1 billion expected in 2023 and the 2.7 billion anticipated by 2025. In short, I think the benefits of 5G are going to take a while to be fully realized.
For another, like any new technology, I still have concerns about security. Researchers at Purdue University and the University of Iowa have already identified as many as 11 new security flaws in 5G protocols, with another 5 vulnerabilities passing over from existing 3G and 4G protocols. While GSMA, the standards body behind the 5G protocols, dismissed the flaws as “nil or low-impact in practice”, their existence should be enough to give IoT vendors pause as they consider whether to step up to this new wireless spectrum.
To Move to 5G, Or Not to Move to 5G
So, should and IoT vendor shift their device to a 5G platform?
Much like the experts at the IOT Solutions World Congress, I think the answer is a qualified yes.
While the slow roll-out of the network and the existence of security flaws are of concern, and while alternatives like Sigfox will continue to offer value for some use cases, the strengths of a 5G network over the current market-leading 4G networks offer advantages that cannot be understated, in particular in four key areas.
- Transmission Speed: True real-time access to data and devices, and the capacity to process more of that data in the cloud means less internal memory on individual IoT devices, and a subsequent drop in manufacturing costs.
- Latency: With lower latency it will be possible for IoT devices to control manufacturing plants, vehicles, and precision instruments remotely, empowering everything from automated transport systems to remote surgical procedures.
- Greater Number of Connected Devices: The increase in bandwidth presents an enormous opportunity for the IoT sector with the possibility for more than a million connected devices per square kilometer all operating at 5G speed.
- Network Slicing: 5G allows for the implementation of virtual networks, also known as network slicing, that allow manufacturers and users to provide connectivity adjusted to specific needs. Connections can be prioritized, and latencies adjusted in order to ensure network robustness in the face of an overload or crisis.
When Will You Shift to 5G?
While 5G technology is being sold on the basis of the enormous consumer benefits it will offer, many of those benefits will flow from the embrace by IoT vendors of the possibilities of the 5G spectrum. As roll-out of 5G networks continues apace and 5G enabled devices begin their inevitable market penetration, I believe the IoT vendor that is prepared for evolution to this new network protocol will surely reap a first-to-market advantage.


